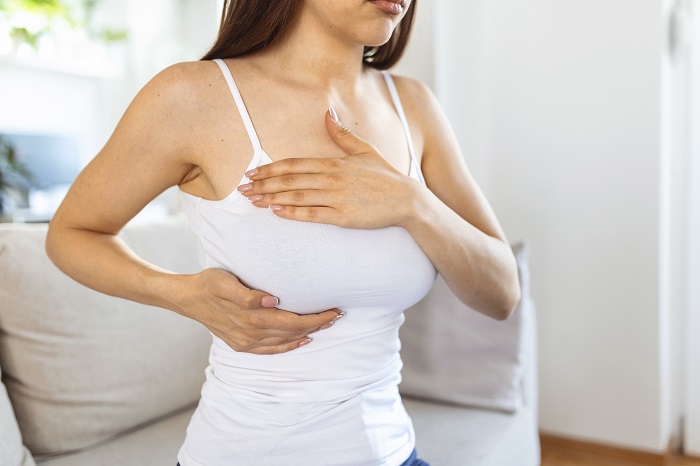
Breast cancer is a disease characterized by the uncontrolled proliferation of breast cells. The type of this cancer is decided by which breast cells become malignant.
Breast cancer can begin anywhere within the breast. The three major components of a breast are lobules, ducts, and connective tissue. The lobules glands produce milk. The tubes that deliver milk to the nipple are called ducts. Connective tissue (fibrous and adipose tissue) encompasses and binds everything together. Most types of breast cancers originate in the ducts or lobules.
This malignancy can spread beyond the breast through the blood and lymph arteries. It is considered that cancer has metastasized when it has spread to other places in the body. Arimidex Pill Used to Treat Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer Variants
The following are the most prevalent kinds of breast cancer:
Invasive carcinoma of the ducts The cancer cells originate in the ducts and subsequently spread to other areas of the breast tissue. The process through which invasive cancer cells spread to other places of the body is called metastasis.
Invasion-based lobular cancer Beginning in the lobules, cancer cells spread to neighboring breast tissues. These invasive cancer cells are capable of spreading to other areas of the body.
Other uncommon breast cancer kinds include Paget’s disease and medullary, mucinous, and inflammatory breast cancer.
DCIS is a form of breast cancer that can evolve into an invasive form. The cancer cells have only spread to the lining of the ducts and have not migrated to other breast tissues.
What Are the Indicators and Manifestations of Breast Cancer?
Symptoms of breast cancer differ from person to person. Some individuals exhibit no indications or symptoms.
Among the breast cancer warning signals are:
- A new breast or armpit mass (armpit).
- Breast enlargement or thickness in a particular place.
- inflammation of the breast skin or dimples.
- Skin discoloration or scaling around the nasopharynx or breast.
- Pulling or pain in the nasolabial folds
- Blood might be present in nipple discharge in addition to breast milk.
- Any alteration in breast size or form.
- Breast discomfort in any region
Remember that these symptoms may be caused by diseases besides cancer.
Make an appointment with your physician immediately if you experience any concerning signs or symptoms.
What Constitutes a Healthy Breast?
Lack of breasts is the norm. What one woman considers normal may not be the same for another. The majority of women have breasts that are lumpy or uneven. Having your period, having children, losing or gaining weight, and taking specific drugs can all affect the appearance and texture of your breasts. Likewise, breasts fluctuate as women age. Breast Conditions and Changes at the National Cancer Institute contains additional information.
What Do Breast Lumps Signify?
Multiple illnesses, including cancer, can produce breast lumps. The majority of breast lumps, however, are caused by other medical issues. The two most prevalent causes of breast lumps are fibrocystic breast disease and cysts. The noncancerous breast alterations caused by the fibrocystic disease include lumpiness, tenderness, and pain. Cysts are fluid-filled sacs that can occur in the breast.
What Are the Risk Factors for Breast Cancer?
Multiple variables increase your chance of breast cancer, according to a study. Being female and aging are the two most significant risk factors. The majority of breast cancers are diagnosed in women aged 50 and older.
Despite the absence of any known risk factors, some women will acquire breast cancer. The presence of a risk factor does not necessarily indicate the presence of a disease, and not all risk factors have the same impact. Although the majority of women have some risk factors for this malignancy, the majority of women do not develop it. If you have these cancer risk factors, discuss risk reduction strategies and breast cancer screening with your doctor.
You are unable to alter the risk factors.
Growing older. Aging increases the risk of breast cancer. The vast majority of these malignancies are diagnosed after age 50.
Changes to the DNA. Women who inherit abnormalities in particular genes, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, have an increased risk of developing breast and ovarian cancer.
History of reproduction Beginning menstruation before the age of 12 and menopause after the age of 55 increases a woman’s breast cancer risk by exposing her to hormones for a longer length of time.
Possessing large breasts. The presence of more connective tissue than fatty tissue in dense breasts can make it difficult to detect tumours with a mammography. This malignancy is more prevalent in women with thick breast tissue.
Personal experience with this cancer or with non-cancerous breast conditions. Women with a history of breast cancer Pills are more likely to treat it again. Breast illnesses that are not malignant, such as atypical hyperplasia and lobular carcinoma in situ, are associated with an increased chance of developing breast cancer.
There is a history of breast or ovarian cancer in the family
A woman is more likely to acquire this cancer if her mother, sister, or daughter (first-degree relative) or several family members on either her mother’s or father’s side have had breast or ovarian cancer. If a woman has a first-degree male relative who has this cancer, her risk is raise.
treatment with radiation therapy in the past. Women who got chest or breast radiation therapy before the age of 30 (for example, to treat Hodgkin’s lymphoma) have an increased risk of developing this cancer later in life.
Diethylstilbestrol (DS) exposure (DES). Some pregnant women in the United States were administered DES to prevent miscarriage between 1940 and 1971. Women who used DES during pregnancy or whose mothers did so are more likely to get this cancer.
Variable Danger Factors
Two women strolled while carrying a dumbbell in each hand. Physical activity can reduce the likelihood of having this malignancy.
Lacking physical activity. Lack of physical activity increases the risk of developing breast cancer in women.
Being overweight or obese after menopause Being overweight or obese after menopause increases the risk of having this malignancy.
Hormone treatment. Some forms of hormone replacement treatment (those containing both estrogen and progesterone) used for more than five years during menopause can raise the risk of this malignancy. Certain oral contraceptives (pills for birth control) have also been associated with an increased risk of breast cancer.
Having your first pregnancy beyond the age of 30, not nursing, and never having a full-term pregnancy can raise your risk of acquiring this cancer.
Having a drink. According to a study, the greater a woman’s alcohol use, the greater her risk of developing this cancer.
According to the study, additional breast cancer risk factors include smoking, exposure to carcinogenic chemicals, and changes in other hormones due to night shift work.
Who Is Susceptible to Breast Cancer?
A family history of cancer increases the risk of developing cancer in both sexes.
This article Health Issue describes how this cancer can be transmitted through families, putting both men and women at risk.
If you have a significant family history of this disease or inherited mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, you may be at a greater risk of acquiring this cancer. You can also increase your risk for ovarian cancer.
Consult your physician about strategies to lessen your breast cancer risks, such as breast cancer medications that block or reduce estrogen levels or surgery.